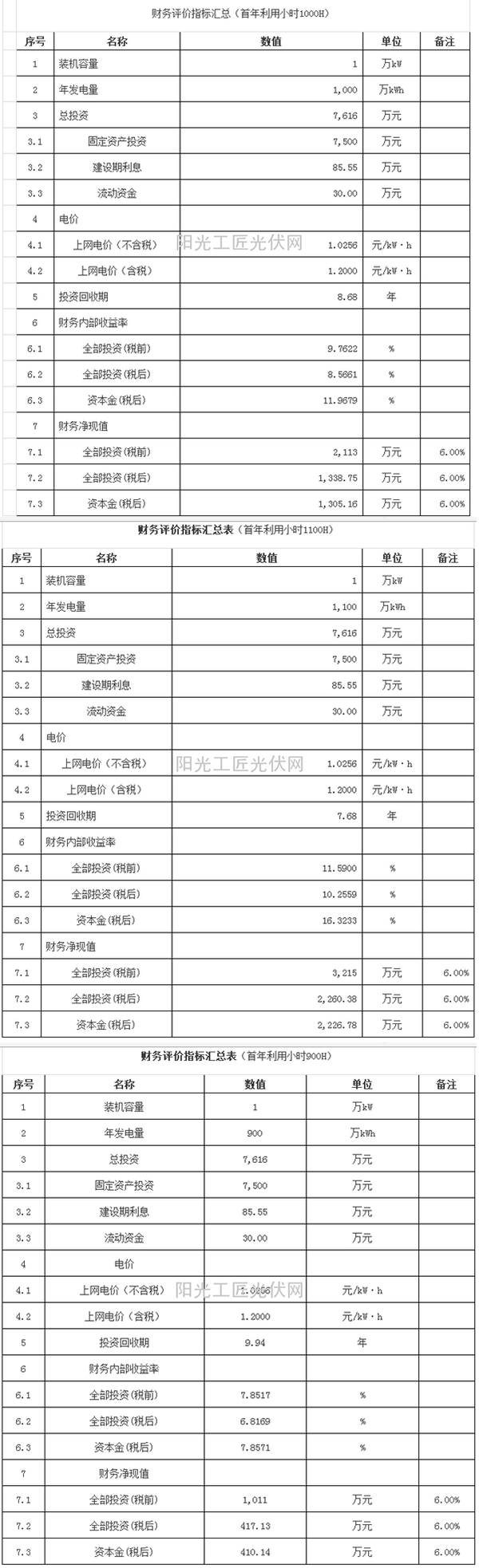
With the maturing of the photovoltaic industry, the requirements of the industry for meteorological data are also increasing. This requires careful analysis of meteorological information in different regions and a careful comparison of different meteorological databases. In order to accurately estimate the benefits of photovoltaic power generation. 1.1 Meteorological Database 1.1.1 Official Meteorological Bureau Database When a project is established, it is necessary to start preparation of a feasibility study report. In the preparation process, the project's power generation needs to be estimated. Under normal circumstances, the local ground-based meteorological radiation observation data can be obtained from the local meteorological department. Generally, the meteorological data for the first five years of the project site can be purchased. Meteorological data is relatively accurate, but it is expensive. Usually, the price of meteorological data in a region is over 10,000 yuan, or even tens of thousands of yuan. Of course we can also get some weather station data from the internet. For example: "Human and Land System Database of the Chinese Academy of Sciences" However, the data recorded in this database is from 1951 to 1980's meteorological data. The record date is too long. We can also obtain database data of a relatively recent age by purchasing data. For example, the “Special Meteorological Data Set for Analysis of Thermal Environment in China†includes meteorological data for the period 1971-2003, which has certain reference value for professionals. The official website of the China Meteorological Administration has the most up-to-date data, but it requires secondary core membership (non-profit research institutes) and the PV power plant is a for-profit organization. This data is not easily available. 1.1.2 Meteorological Data Obtained by Third Parties 1.1.2.1 METEONORM Software METEONORM's data are sourced from the Global Energy Balance Archive, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO/OMM) and the Swiss Meteorological Agency and other authoritative organizations, including radiation data from 7750 weather stations worldwide. There are 98 meteorological radiations in China. The observatory is included in the software's database. Through the 6.0 version of the software, the average annual radiation of the meteorological radiation station for many years from 1981 to 2000 can be searched (for the 7.0 version, it is the average monthly radiation for many years from 1990 to 2005). In addition, the software also provides other multi-year average monthly radiation doses obtained by interpolation methods at any other location without meteorological radiation observation data. 1.1.2.2 NASA Ground Radiation Database The NASA ground radiation database is based on satellite observations of the top of the atmosphere radiance, cloud distribution maps, ozone layer distribution maps, and suspended particle distribution data. The global surface water level total radiation data is obtained through complex modeling and calculations. Then, the scattered radiation and normal direct radiation (DNI) data of the horizontal plane are derived from the total radiation of the horizontal plane according to the relevant formula. “Cloud†refers to a collection of water droplets or ice crystal colloids that stay on the atmosphere. Light rays refract, scatter, and weaken when they pass through these water droplets and ice crystal colloids. In order to achieve the reduction of the reflected light of the satellite and the deviation between the imaging and the actual position, the image is reflected in the unclear and dark. In southern China, especially in the area south of the Yangtze River, the water network spreads vertically and horizontally. Vapor evaporation forms a relatively thick cloud layer in the troposphere because satellites are affected by factors such as clouds, airborne materials, and large bodies of water. The data gap between NASA's data and general ground weather stations is very large. (See Table 1-1) Areas in northwestern China such as Xinjiang, Inner Mongolia, Qinghai, and Gansu are open, dry, and have better solar radiation. Radiation data from self-prepared meteorological stations of photovoltaic power stations that have already been built (less ground-based observatories in the deserts in the northwest part of the country) are not significantly different from those in the NASA database. 1.1.3 Self-contained weather stations Some EPC companies or professional PV companies also have their own weather station data. For example, the weather stations in Shanghai from January to August 2014 provided by Shanghai Taoke are listed in Table 1-1. The solar radiation data of the official meteorological bureau is collected every minute, and the professional photovoltaic meteorological station collects meteorological data (irradiance, wind speed, and temperature) every 0.5 seconds to 1 second, and the accuracy is relatively high, which is very useful. Table 1-1 shows the irradiance data of (28°) under the best inclination in Shanghai. In 2014, the actual measured irradiance data and the Meteonorm data have a small difference, while the data of NASA (referred to in this article with reference to the RETSCREEN own data) is relatively large and the data differs by 30%. 1.1.4 Data Accuracy Analysis of China's Ground Meteorological Stations before 2004 As China's photovoltaic industry started relatively late, the collection of solar radiation data is not detailed or comprehensive. Most of the data were recorded at a time interval of 3 hours, and many missing data were obtained using mathematical interpolation. Some weather stations do not initially include solar radiation data. Many data are derived from known weather data. In the 1990s, China implemented a meteorological radiation observation method to classify radiation observation stations at the first, second, and third levels. Only the first-level stations have comprehensive observation data: total radiation, scattered radiation, direct radiation, reflected radiation, and net total radiation. The tertiary station only measures total radiation. Since only 1/3 of the 270 stations in the country were capable of observing solar radiation data (more than 90 METEONORM records), the solar radiation data at the remaining stations was calculated based on the formula. This kind of data has lost its use value in power generation estimation. Since more than 90 meteorological station data are collected by METEONORM in China, the weather station data in the METEONORM database is also accurate. Moreover, METEONORM software is currently charged for service fees, and the cost of services is high. We are currently able to use free data up to around 1990-2005. 2.1 Impact of Meteorological Data on Project Investment Return 2.1.1 Data Modeling Assume that the project site is located in Nanjing, with a capacity of 10 megawatts, system efficiency of 80%, and 7.5 yuan per watt, and electricity generation for self-use electricity charges of 1.2 yuan per kWh. The operation and maintenance costs are 2 million/year, and the financial parameters such as loan interest rates are in line with the current market. Summary of financial evaluation indicators (first-year utilization hour 1000H) As can be seen from Tables 1-2, 1-3, and 1-4, the 10% deviation of the meteorological data caused a huge change in financial data. It may cause investment mistakes or miss good investment opportunities. The accuracy of meteorological data is very important, and obtaining relatively accurate meteorological data is more difficult. This requires the entire photovoltaic industry to share data, collate scientific systems and analyze the past data exchange. At the same time, the government's meteorological department should classify the data and introduce several data with different accuracy, 1. accurate to the year and month; 2. accurate to the date; 3.3 years and 5 years; at the same time, the data will be accurate to the year and month. It is freely published on the website of the Bureau of Meteorology. For designers who need it for reference.
Wine rack,stainless steel wine rack,Iron wine rack, wine holder,wine bottle rack
wire holder is made of high quality 304 stainless steel, It is easier to clean without rust, safe, healthy and durable, Prevent rust or chemicals from contaminating food and damaging health. Suitable for putting wire bottle.
China leading manufacturers and suppliers of Wine Holder,Wine Bottle Holder, and we are specialize in Wine Rack,Hanging Wine Rack, etc.
wine bottle rack,metal wine rack,wine display rack,Wine rack holder,honeycomb wine rack Shenzhen Lanejoy Technology Co.,LTD , https://www.grill-mesh.com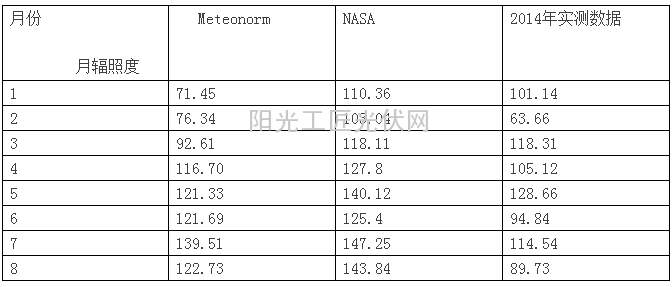
Table 1-1