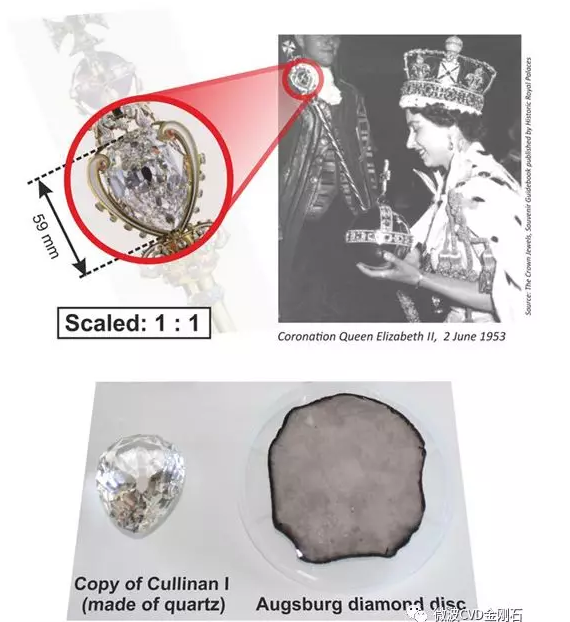
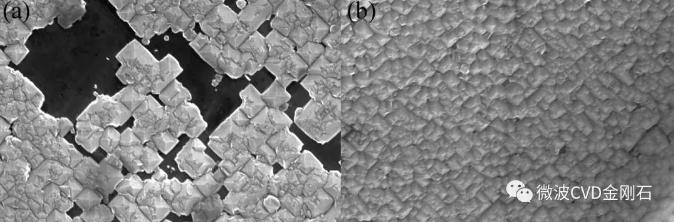
Diamond has wide-bandgap, high thermal conductivity, high carrier mobility, low dielectric constant and other superior characteristics, and has great application value in various fields. Among them, diamond single crystals have become the best choice for diamond applications in the fields of high power and high frequency electronic devices because of their absence of grain boundaries and low defect density. In recent years, the research on homoepitaxial diamond single crystal by chemical vapor deposition has made great progress, but the diamond single crystal substrate prepared by high temperature and high pressure method is difficult to meet the demand in both size and price, to a large extent. The development of a synthetic large-size single crystal diamond film by the homoepitaxial method is limited. In order to find an effective way to synthesize large-area single crystal diamond films, a heteroepitaxial single crystal diamond film by CVD method has been tried. By means of the bias-enhanced nucleation (BEN) technique, one can obtain a high diamond nucleation density on a non-diamond substrate, thereby obtaining a larger area of ​​the diamond single crystal epitaxial layer. During this process, the negative bias applied to the plasma will cause low-energy positive ions in the plasma to bombard the surface of the non-diamond substrate, and this bombardment is considered to be the key to inducing diamond nucleation on the surface of the substrate. step. Based on the bias-enhanced nucleation technique, high-orientation or heteroepitaxial growth of diamond films on substrates such as Si, β-SiC, Ni, Pt, and Ir has been achieved in recent years. Among many optional diamond heteroepitaxial substrates, single crystal Ir films have become diamond heterogeneous due to their small lattice mismatch with diamond, difficulty in forming carbides, high melting point, and easy preparation in large areas. An ideal base material for epitaxy. Applying microwave plasma at 250V bias Over the years, many scholars around the world have tried heterogeneous epitaxy of diamond films in different epitaxial materials such as Ir/MgO, Ir/SrTiO3, Ir/SrTiO3/Si, Ir/YSZ/Si, Ir/CaF2/Si. Great progress has been made. In 2017, the technical team of the University of Augsburg, Germany, used the "hetero-epitaxial growth technology" to synthesize a 155ct CVD single crystal diamond. Although the 92mm diameter "disk" diamond is only 1.6mm thick, the weight of 155ct is enough to shock the world. The 155ct diamond disc made by the University of Augsburg is nearly twice as large as the jewel on the Queen's Scepter In contrast, the development of heteroepitaxial diamond films in China is relatively slow. Only a few scholars have studied the deposition process of high-orientation diamond films. To achieve heteroepitaxial growth of diamond, the first need for a suitable epitaxial substrate, and the second requires proper bias nucleation of the substrate. The latter puts certain structural requirements on the CVD biasing device. For a cylindrical cavity type MPCVD apparatus of a conventional quartz bell-type and quartz flat-panel window, there is a microwave window block for defining a vacuum region above the plasma, which is inconvenient for the device to provide a bias electrode over the plasma. In recent years, the laboratory has made great progress in the development of MPCVD equipment. The tunable cylindrical cavity type MPCVD diamond film deposition device developed by the laboratory has a unique structure and is especially suitable for designing a bias-reinforced MPCVD device. Our unit used an improved bias-enhanced MPCVD device to attempt diamond heteroepitaxial nucleation on Ir(100)/MgO(100) substrates and achieved significant results. The surface topography of the diamond heteroepitaxial core: (a) pyramidal epitaxial diamond-shaped nucleation particles that tend to be continuous; (d) closely aligned epitaxial diamond nucleation particles Heterogeneous epitaxy of diamond involves the preparation of heteroepitaxial substrates, bias-enhanced nucleation, and diamond growth. Although the self-developed bias-enhanced MPCVD apparatus achieves heteroepitaxial nucleation of diamond on the surface of Ir. However, there is still a long way to go to achieve a large-area heteroepitaxial high-quality single crystal diamond film. The technical team at the University of Augsburg in Germany was able to produce a diamond disc with a diameter of 92 mm and 155 ct, which took 26 years. China started late in this field, but we must have the spirit of catching up and catching up. We will soon realize the preparation of China's large-size single-chip and super-large diamonds, and promote the progress of China's related industries. With years of experience of tools production and assembly together, Newstar Hardware is very strong at Household Tool Set in different combinations: household tool set in blow box, household tool set in aluminum case, household tool set in bag, different colors and sizes per customer needs. We offer OEM and ODM services on household tool set, open ideas on new design and help customer with big quantity orders. Household Tool Set,Home Tool Kit,Mini Tool Kit,Household Toolbox SUZHOU NEWSTAR HARDWARE CO.,LTD. , https://www.newstarhardware.com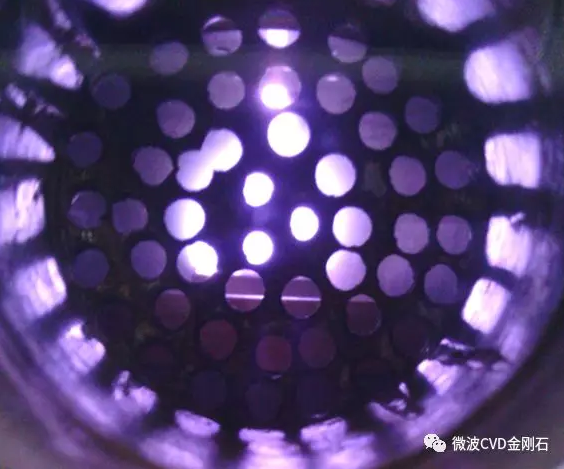
"Extra large" single wafer and "super large" diamonds grow: diamond heteroepitaxial
Abstract Diamond has great properties such as wide band gap, high thermal conductivity, high carrier mobility and low dielectric constant. It has great application value in various fields. Among them, diamond single crystals have become the current high-power and high-frequency electronic devices in diamonds because they have no grain boundaries and low defect density...