The combustion process of wood and other biomass includes open flame burning of volatile matter and burning of residual coke (residual carbon). Compared with open flame combustion, the burning of residual charcoal can be maintained under extremely oxygen-deficient conditions, has the characteristics of mild reaction and long duration, and can trigger violent open flame combustion again when the ventilation conditions are good. The research on the burning mechanism of residual carbon is of guiding significance for the efficient and clean burning of biomass, as well as the early warning and rescue of forest fires and wood building fires. In recent years, the Thermal Energy Engineering Research Group of the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Processes, Chinese Academy of Sciences has cooperated with the Energy Research Center of the University of Western Australia in Australia and the Energy Engineering Laboratory of Toyohashi University of Technology in Japan to carry out a series of research work on the above issues. The researchers selected activated carbon particles as a model of biomass carbon residue, and carried out experiments using a fixed-bed reactor under controlled boundary conditions. They successfully captured the quasi-steady-state spreading process of the flaming front, and investigated the effects of the physical and environmental parameters on the carbon residue. The influence law of combustion characteristics. Through computational fluid dynamics simulations, the researchers mathematically analyze the heat and mass transfer phenomena and chemical reaction processes in the burning process, reproduce the spreading process of the burning front, predict the thermochemical structure of the burning front, and reveal the biomass carbon residue. Burning mechanism. This study shows that the heat release of gas phase components such as carbon monoxide has surpassed the surface oxidation of fixed carbon to become the dominant factor under some conditions. This discovery completes and develops the conclusion that the ignition process is dominated by heterogeneous surface oxidation reactions. The relevant results were published in the Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, and were accepted as oral reports by the 38th International Combustion Conference. Based on the above results, Dr. Huang Xinyan of Hong Kong Polytechnic University and Dr. Gao Jian of Qingdao Energy Institute published a review article A review of near-limit opposed fire spread in Fire Safety Journal, which further explained the burning mechanism of flaming phenomenon, Smoldering and other combustion phenomena are clearly distinguished. The research was supported by the start-up funding of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Qingdao Institute of Energy Research. Our LED Emergency Batten Light is perfect for commercial and industrial use, made from solid polycarbonate with a thick poly carbonate diffuser the unit is very durable this fitting has an IP rating of 65 and is anti corrosive. Interal lithium battery pack to make emergency time rating from 60-180mins. The fitting gives off an impressive 5850 lumens using only 65 watts of energy making it a great energy saving light fitting. The batten uses high quality LED chips giving off a great array of light to any indoor and outdoor area. Emergency Batten Light,Emergency Led Batten,Emergency Light Batten,Led Emergency Batten Light Foshan Nai An Lighting Electric Co.,ltd , https://www.fsnaipsled.com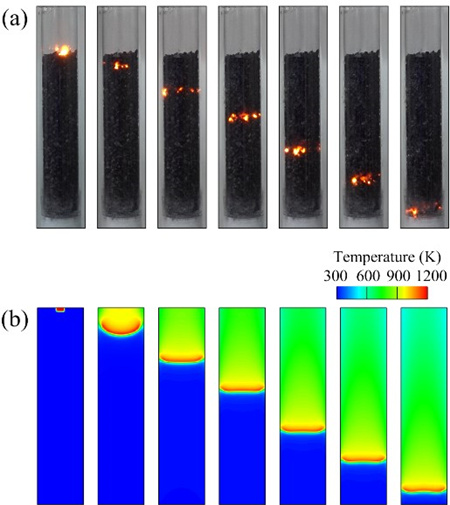
The spread of the flaming front: (a) experimental phenomena, (b) simulation results